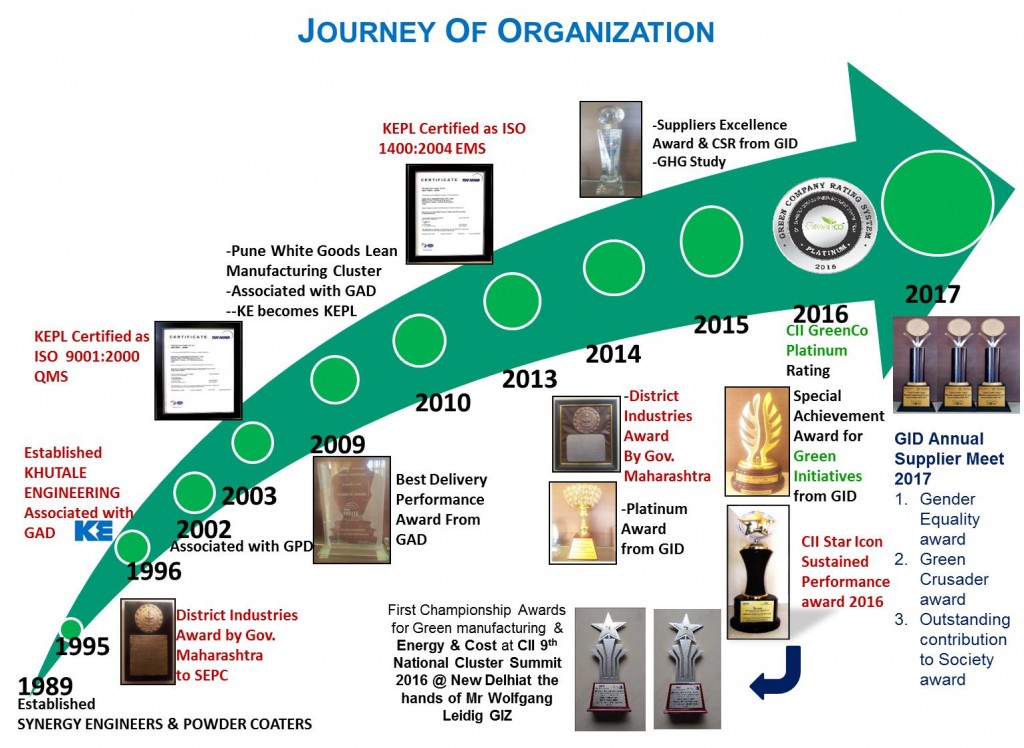
Khutale Engineering.
Your case study will be evaluated based on following criteria. Shortlisted case studies will make final presentation at the National Productivity Summit 2019.
PARAMETERS FOR PREPARING CASE STUDY AND CRITERIA FOR SELECTION :
- Need for implementing the project
- What solutions did you come up with
- How was it implemented
- What challenges did you face while implementing it and how was it overcome
- Benefits to Organization from this project, such as Cost reduction, Reduction in manpower, Increase in Output, Reduction in rejections / internal wastes etc.
Note : Please consider the above points as guidelines and elaborate as appropriate.
PRODUCTIVITY IMPROVEMENT USING LAYOUT PLANNING
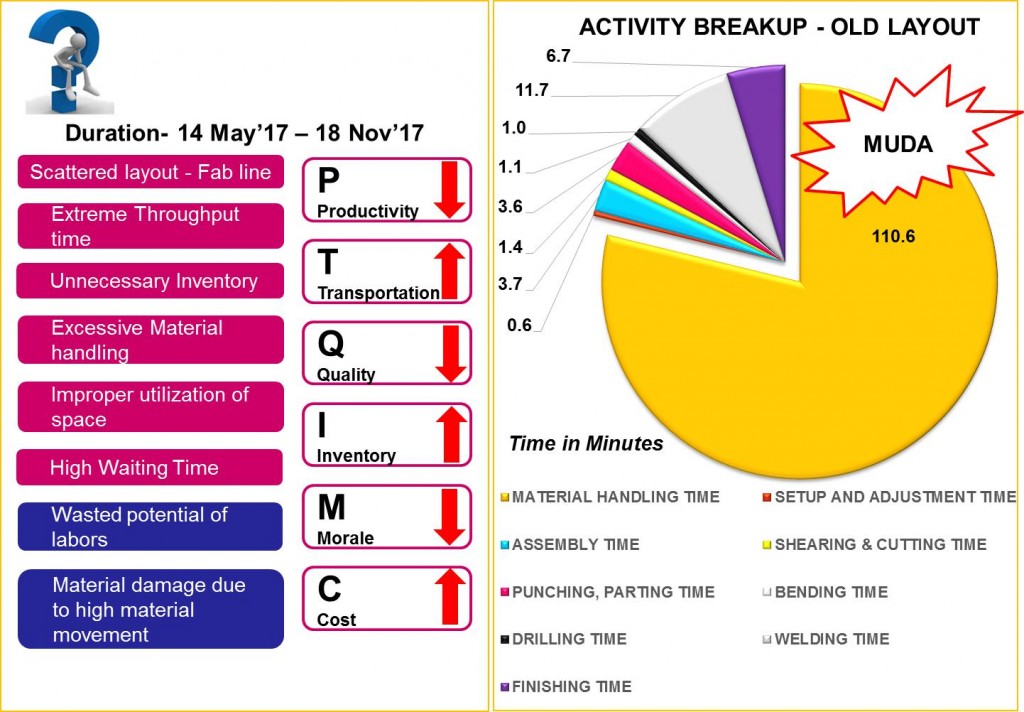
Need for implementing the project
Problem Identification : <Why the Project was Selected?>
Data Collection : <What data was collected?>
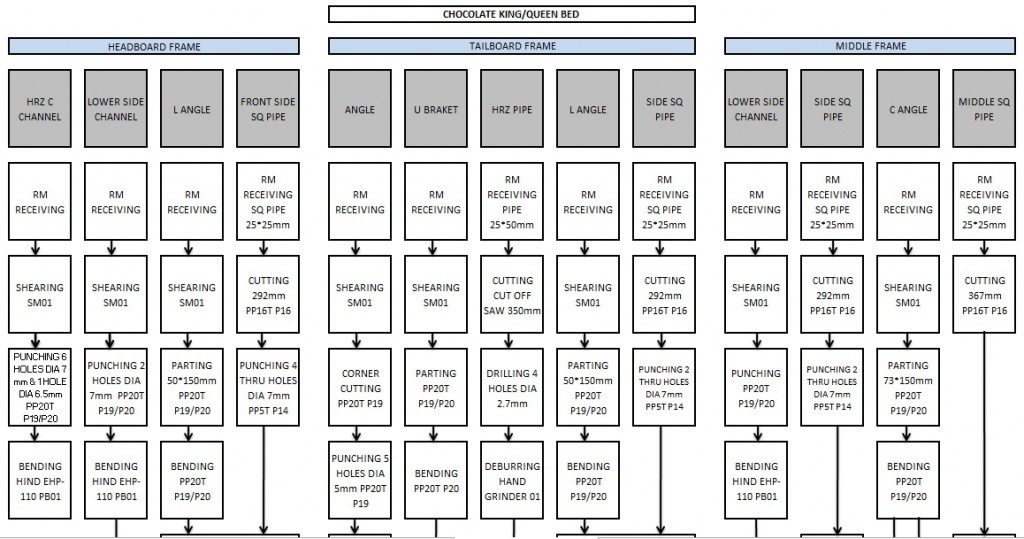
- Detailed study of Product and processes
- Materials flow – Flow Chart, String Diagram
- Flow Process Chart for identifying various type of wastes
- Cycle time of various products
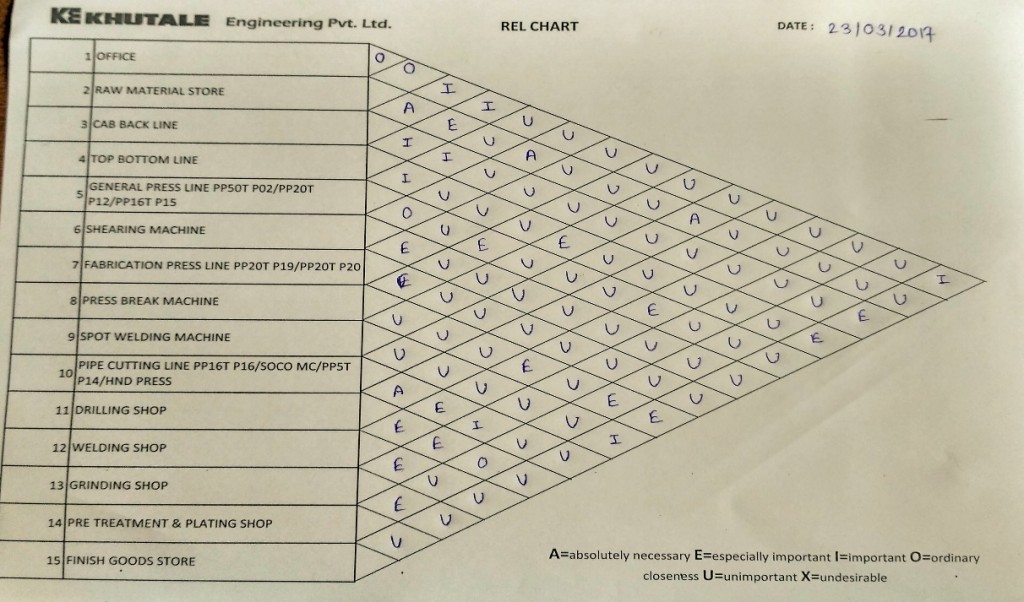
- Relationship between departments – REL Chart
- Determination of plant capacity – Products, Quantity data of 6 months
- Available Space
- Dimensions of existing layout, machineries, utilities etc.
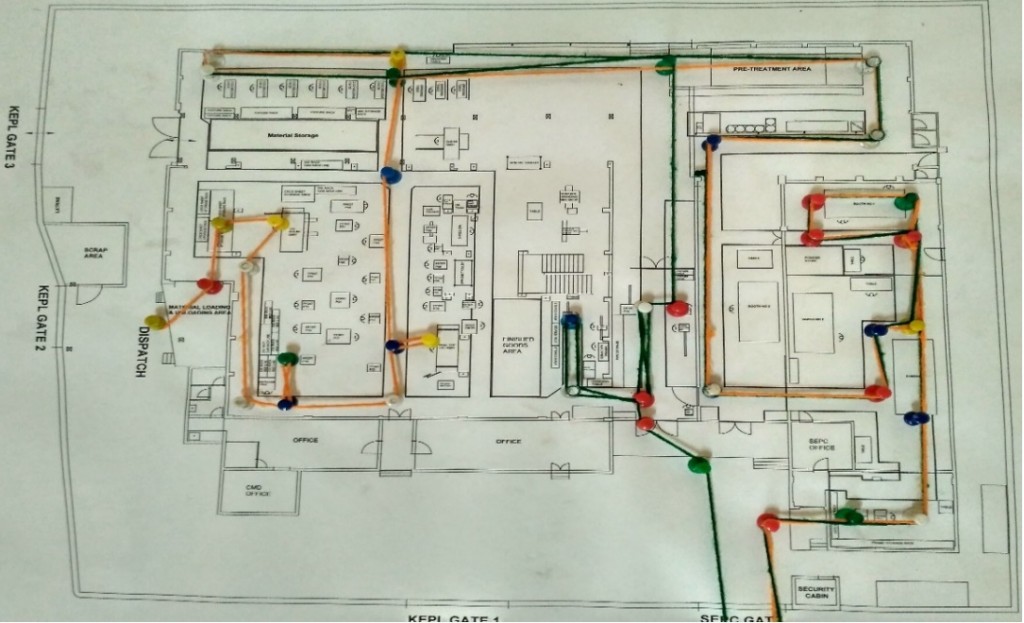
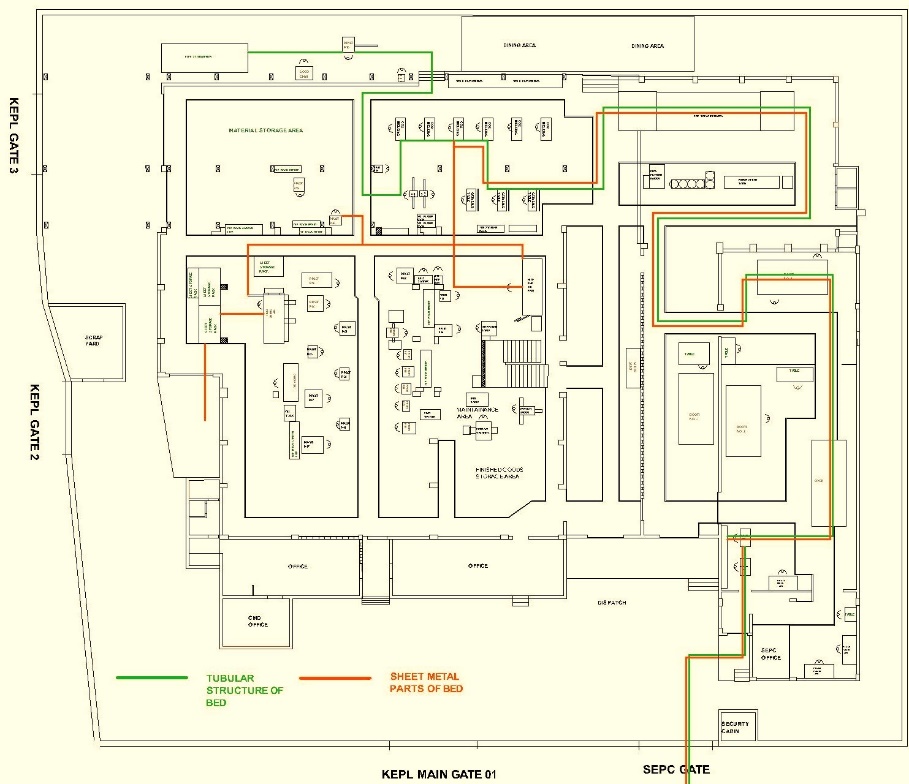
Past Layout : String Diagram of Chocolate King bed
Flow Diagram : Chocolate King bed
REL Chart
What solutions did you come up with?
Analysis and Development of Solution :
< What analysis was carried out?>
< What were alternate solutions proposed? >
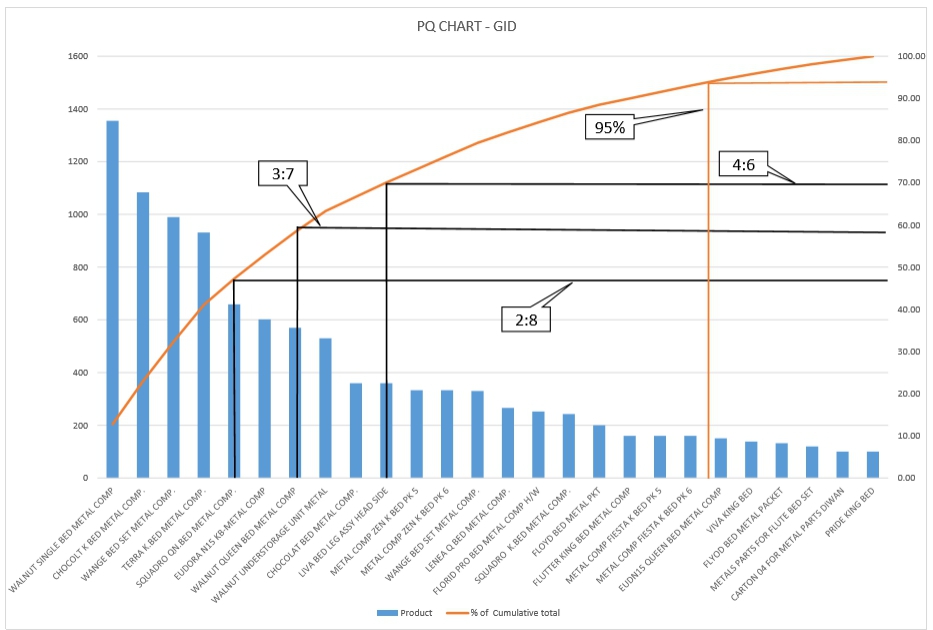
- Product & Quantity – PQ Analysis
- Got runner, repeater and stranger products
- Layout redesigned as per runner products
- Walnut bed is highest demanded product while it requires minimum processes so it was not considered for study.
- Chocolate, Wenge, Terra, Squadro, Eudora, Flutter are those beds whose metal frames and sub components are similar and requiring maximum processes so, to represent all above-mentioned beds only chocolate bed is considered for study.
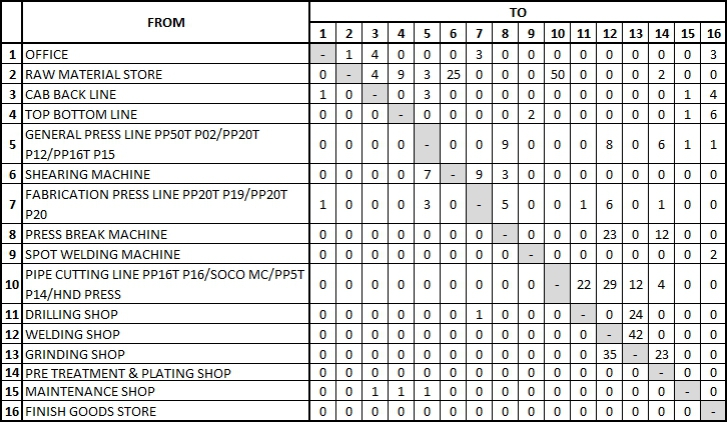
- Flow of material analysis – From-To chart
- Activity Relationship Diagram
- Space Requirement and available analysis
- Flow analysis is performed on dimensionless block diagram or space relationship diagram
For example :
PQ Chart
From - To Chart
How was it implemented
Implementation :
< Why was the particular solution chosen?>
< How was the chosen solution tested/validated and implemented?>
< How effectiveness and sustenance of action monitored?
Solution selection and evaluation phase:
Based on analysis :
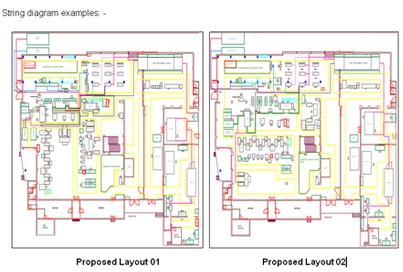
- String diagram of all proposed layouts were drawn
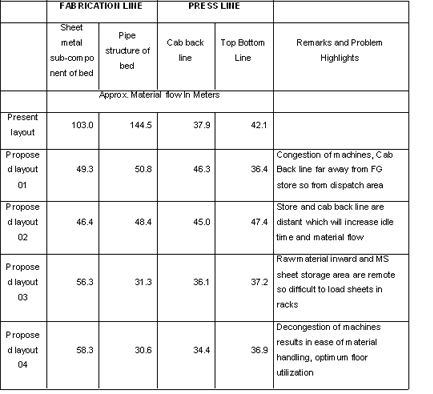
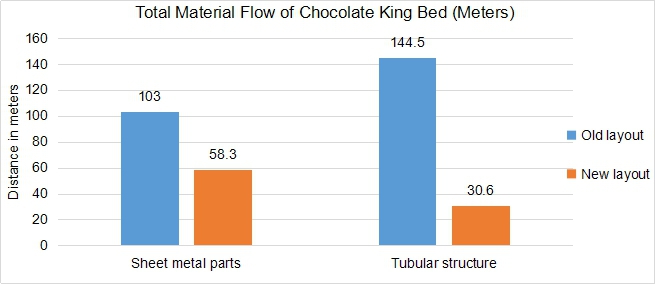
- Material flow distance of selected products of present layout and all proposed layouts were compared
- Pros and cons of each proposed layout were discussed
- Layout which was flexible, had ease in material handling and utilizes optimum floor space was selected
String diagram examples :
Proposed Layout 04
- To validate the chosen solution, we used CORELAP Algorithm
- CORELAP Algorithm uses shortest path between departments
- Dimensions of machines, equipment’s, racks, aisles of a selected layout were marked on floor
- As per markings machines, racks were placed at their particular positions
After implementation phase :
- Cycle time study was conducted
- Removed all practical constraints
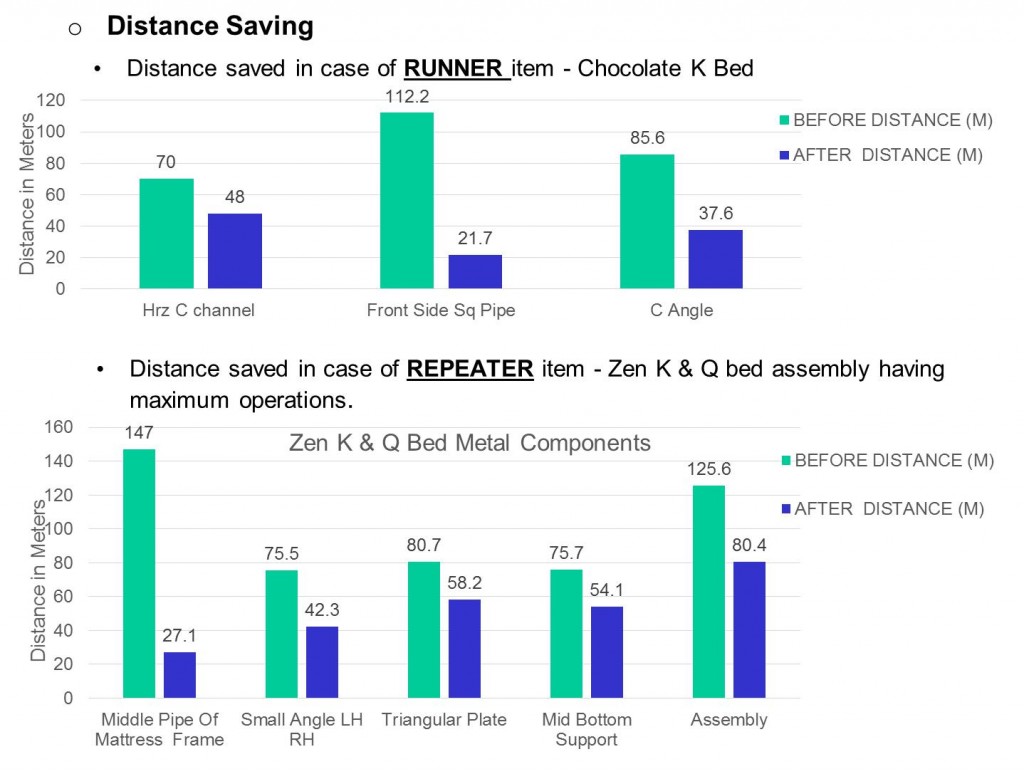
- Distance traveled by selected product was calculated and compared with its distance in past layout
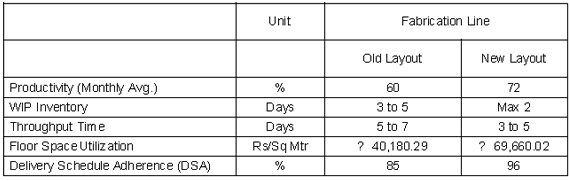
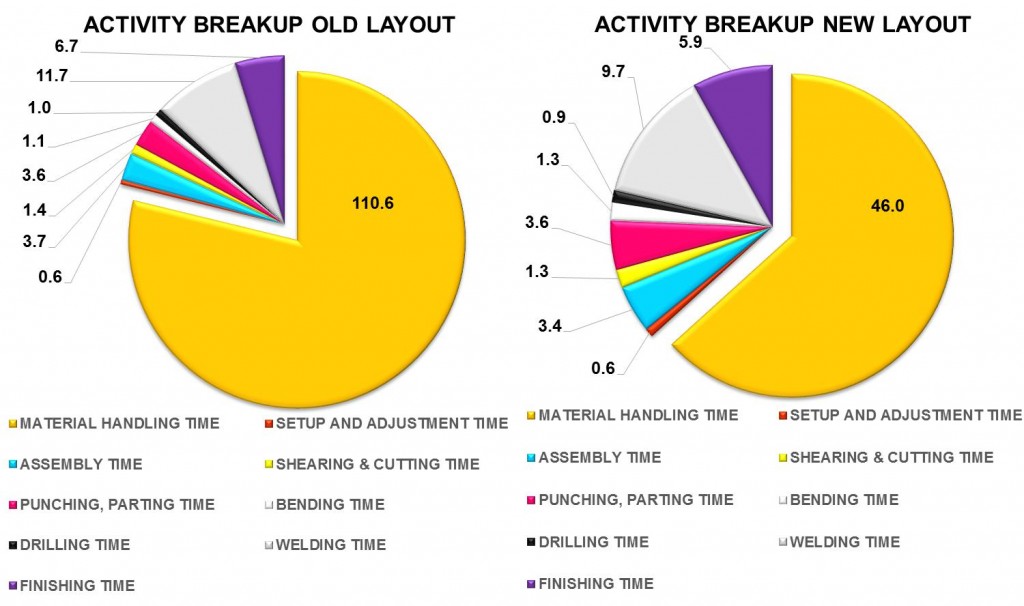
- Results of following parameters such as travelling time, distance, daily production were compared
What challenges did you face while implementing it and how was it overcome
- Building demolished as per layout
- Construction ofnew building inside factory premises which hampered production, dust, rain, noise & congestion issues.
- Manpower loss
- Problems while shifting / relocating heavy machinery
- Dents & damages of raw material and finished goods during shifting
Benefits to Organization from this project, such as Cost reduction, Reduction in manpower, Increase in Output, Reduction in rejections / internal wastes etc.
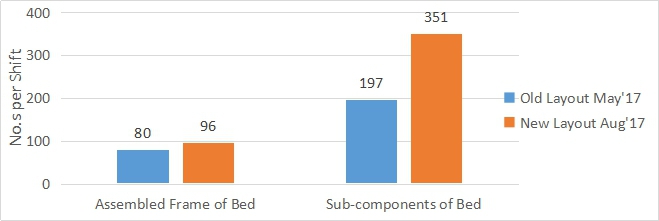
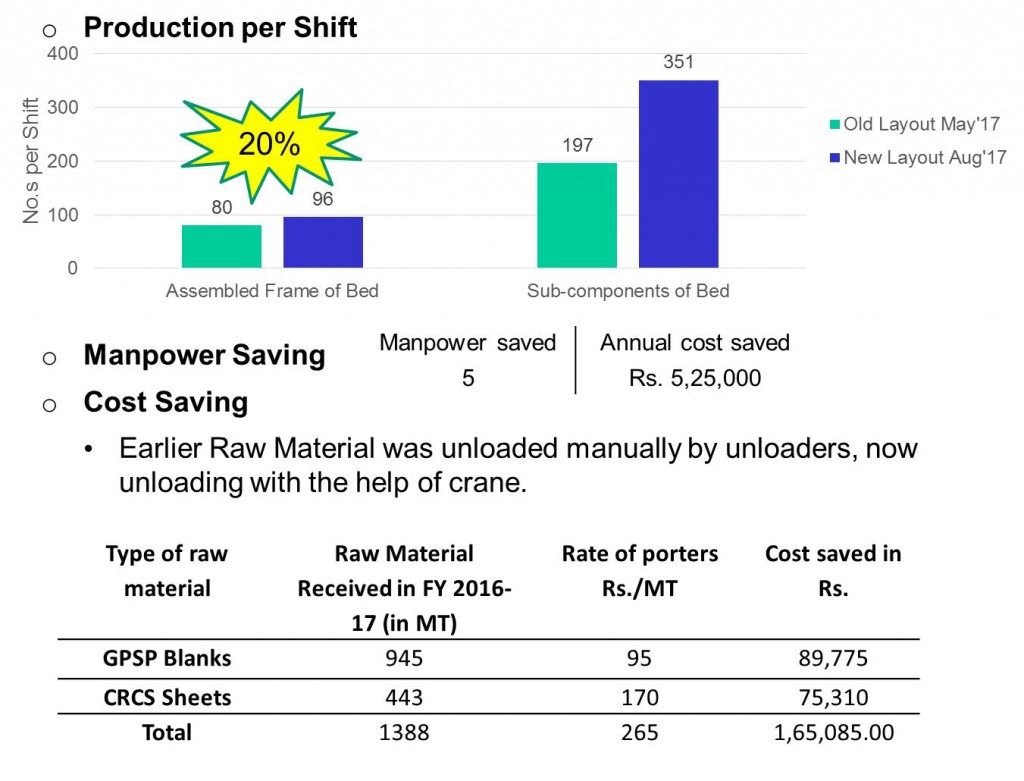
Production per Shift
Intangible Benefits:
- Productivity increased
- Throughput time decreased resulting into 100% Delivery Schedule Adherence (DSA)
- Ease of material handling & optimum space utilization
- Labor multitasking achieved
- Raw material under one roof ease in unloading of Raw material thus improved inventory control
- Employee morale boosted