Brakes India Private Limited
- Description of our Case study / Project :
Improving the aesthetic look of the casting is the key in winning the business from high-end car market.
The final qualities like material property and dimensional consistency are taken for granted. Achieving good quality in the part finishing is the real challenge which is becoming rapidly an entry barrier for many foundries. The process technology and tooling technology needs to be on the top notch to achieve this.
As the effects of TQM/TPM practices in Brakes India – Foundry (BIF) focussing on the process technology resulted in breakthrough improvements and consistently winning business from many automakers as a tier 2 supplier. In the recent past, the aesthetic look of castings is becoming more of a quality parameter where automakers like AUDI started giving specifications to tier 2 and tier 3 suppliers on surface finish and aesthetic look. Focus on the process as well as tooling technology, is becoming more imperative. BIF started in this direction, a couple of years ago and have progressed well on this. The structured study on this direction revealed that the tooling quality is one of the most important parameter in the path of achieving better casting finish. Utilization of technology on cutting materials has been intensified by structured and focussed experimental methodology.
This has resulted in the castings with all the aesthetic features that are being envisaged by the ultimate customers – Car owners.
- Trigger for the project :
The trigger started in five ways, which are given below.
- The repeated customer dissatisfaction on the clumsy fettled finish of our castings.
- The stress marks created on the casting due to excessive fettling which reduced the fatigue life of the casting.
- Variation in the casting geometry and casting weight.
- Inconvenience to customer/ tier 1 supplier during machining and assembly.
- Difficulty in meeting NVH norms.
- Approach/conceptualization of the project :
This project was started with the scope of improving the parting line size, shape and finish. As parting line on the casting enhances the aesthetic beauty of the casting by retaining the naturally solidified surface all around the casting.
So this project looked at the technology behind the parting line design and tool design covering the tooling material, cutting tool material, machining strategy in CNC machine and design on 3D modelling. The whole of these will be studied along with their interaction of the process technology and a holistic sustainable and cost effective solution to be developed. There were many experiments and trials conducted on the process technology, viz moulding where various parameters like sand mixing and moulding machine settings were optimized. Considering the limitations on the quality of raw materials available in India, the optimizations were carried out. In this project we had to combine the process technology with tooling technology to achieve best results.
The other aim of the project was to make the tooling technology to have less manual dependency as the parting line were being finished by skilled man using hand held tools. The innovation was, in adopting right combination of technology and the development of a matrix, which is unique for each type of products and its tooling because, different shapes of casting requires different technique.
There were many approaches contemplated to achieve the good look of the casting from the tooling side. They are given below along with their merits / demerits.
Approach 1 :
Making the tooling with the best available, in the best in class pattern shops in the world. This approach could give quick results by readily giving the solution and we could be on par with our competitors. But this approach is not suitable because
- It would not significantly improve our knowledge for the future.
- Increased dependency on their pattern shops where they have queue and waiting periods. Our 'Time to market' will not be in our control.
- High cost.
- It did not address the most important factor - the interaction of tool design with our manufacturing process.
Approach 2 :
Tool making by using 3D printing techniques. This approach was not pursued because,
- The limitation of the size that can be printed.
- Cost of implementation.
- Capacity constraint.
- Though this is an emerging technology, still pattern shops using the machining techniques against 3D printing due to various advantages other disadvantages.
Hence we decided to go for approach 3, in which, machining the tooling ourselves in our pattern shop, doing experiments and studying the results, till the desired improvements are achieved.
Approach 3 :
This has the advantages of understanding the entire chain of sub processes introducing best-in-class technique appropriately, experimenting and optimizing.
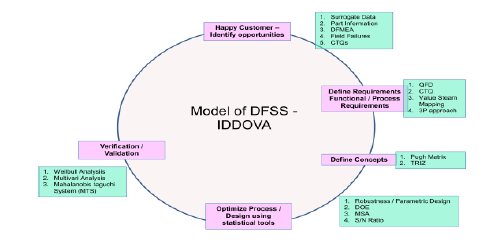
Utilization of the DFSS (Design for Six Sigma approach), has provided us the direction effectively.
- Project Planning :
The project started in 2014. The following are the phases in the project:
- Identify the opportunities
- Define requirements
- Define concepts
- Optimize the process/design using statistical tools
- Verification/ validation and Standardization.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Aesthetically good looking casting recognized by customer
- Least manual intervention in tool making
- Least content in fettling of casting and reduction in manpower
- Ease of making tooling
- Reduction in throughput time in casting processing
- Project implementation:
- Understand present situation - What exactly has gone wrong
- How to improve – Improvement kaizens and break through innovations.
- Utilization of virtual machining techniques and simulation.
- Improvement in tool design
- Improvement in tool making method – tool path
- Improvement in cutting speed
- Improvements in tooling materials
- Improvement in surface finish and surface hardness in tooling's
- Poka yoke
- Shop floor trials
- Achievement of objectives.
- Value creation and business sustainability:
The tooling life should have doubled, though we have not seen the end of life of tooling after we made the improvements. Also with new material and technology of tooling, the replacement cost and validation cost of replacement tooling, will reduce or disappear for both BIF and its customers. The maintenance and restoration cost of tooling has come down at least by 50%. There is an increasing difficulty in getting man power for doing manual fettling, as the fettling work is considered as a dirty job by the younger generation work men. Hence investment into the Robot fettling, trimming and CNC fettling are being followed which is all capital intensive. With the new generation tooling, this can be reduced.
Customers started realising that castings have improved aesthetic look, which resulted in continuity of business and new projects. We see improvements in the overall score of our supply ratings. The stake holders who were benefited were:
- Brakes India Foundry as the whole.
- Customers
- Pattern shop in BIF due to reduction in burden due to maintenance.
- Finishing team in BIF due to less work.
- Inspection & quality team due to lesser burden on visual inspection for parting line and other defects.
We are one among the top five suppliers on volume. We want to be on par with other four suppliers, as all these four are located in developed countries, who have access to all sort of technologies at their disposal and closer to customers.
We are able to break the barrier now.
- Any other relevant information that supplements your projects / case study to be winning entry:
Utilization of virtual techniques like simulation for validation of design, simulation of CNC manufacturing was used extensively. We have involved global cutting tool experts for finding the right kind of tools suitable to our requirements. They helped us in optimization.
We have used DFSS (Design for Six Sigma) techniques with experts from “INDIAN STATISTICAL INSTITUTE” by using tools like MAT-LAB and other statistical – analytical techniques.
We were also supported by our customers, right from bench marking. Their SQAs also visited us to evaluate and understand how we were improving.
Project summary :
Factors contributing for fin formation in casting were studied
| S.No | Process Related | Tooling Related |
| 1 | Machine mismatch | Tooling parting line radius |
| 2 | Variation in sand properties | Clearance between to pattern halves |
| 3 | Variation in mould properties, Analysis of air vents |
Clearance in the core print |
| 4 | Variation in cores | Clearance in core mask |
| 5 | Metal temperature | Tooling tolerance |
| 6 | Tooling warpage | |
| 7 | Pin and bush tolerance |
Following parameters were analysed for design finalization of tooling and process. DFSS approach was followed for study.
Short notes on actions and results:
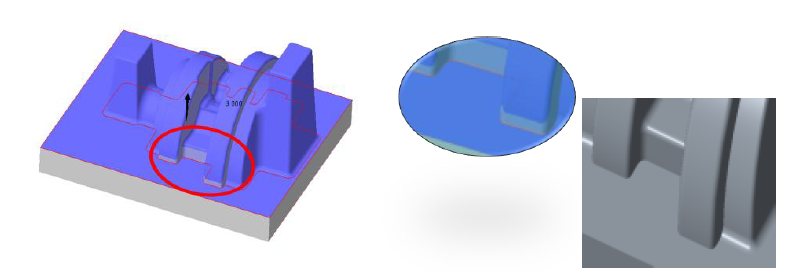
1) Design of tool at parting line was the dominant factor found from experiments. Re-design and poke yoke implemented.
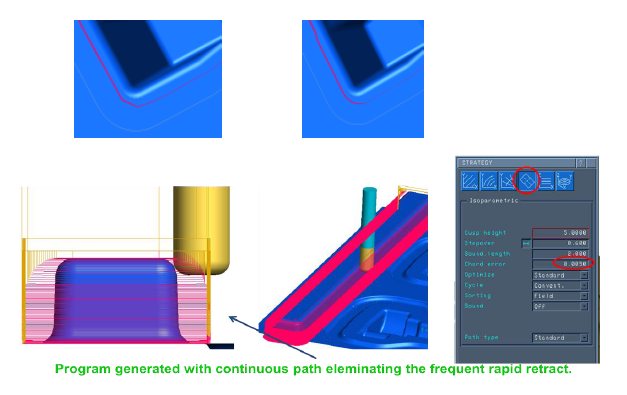
2) Cutting tool length to diameter ratio was found to be a dominant factor. The optimization was just impossible without a simulator. So the technology was updated by introducing a simulation to achieve good result.

3) Tool path have interactions with other parameters which lead to more machining time and quality. DOE were conducted to optimize.
4) Cutting tool and their geometry were significant. Selection and usage of cuter is one of the dominant factors in achieving the surface finishing of the tooling. We collaborated with cutting tool makers to optimize.

5) Tooling materials were optimized based on their properties like aberration resistance and high compactness of grains. In-depth studies conducted and materials were bench marked.
6) Measurement methods have been introduced in evaluating the cutter, cutting tool life and deterioration with respect to other given parameters. We have introduced tool pre-setters for the same.

7) Surface roughness was one of the measures indicating improvement. We have introduced this quantitative measuring technique.

8) The post machining finishing has also been improved by utilization of better hand tools.
End results:
Surface finish of the tooling reduced from 5 micron to less than 2 micron
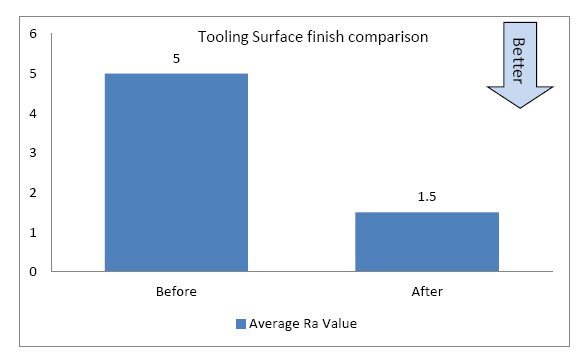
RESULTS
1. Surface finish of tooling improved from Ra = 5 to Ra < 1.5
2. The surface finish of the casting has improved from Ra > 40 to Ra < 20
3. Fettling content in the casting is restricted to only gate area and there is no fettling on other partingline.Thus reducing the content of fettling by about 60%. There is a huge saving out of fettling reduction.



